Chromosome Disorders
Changes in Chromosome Number
The four main results of cell division. Terms in this set (4) Reproduction. In some unicellular organisms, cell division is a form of asexual reproduction. Get an answer to your question “What are the 4 results of cell division?” in 📙 Chemistry if there is no answer or all answers are wrong, use a search bar and try to find the answer among similar questions. The cell cycle results in the formation of two genetically identical daughter cells from the division of a parent cell. In this lab you will be observing plant cells (onion) in the various stages of mitosis, and make time calculations based on the data you collect.
Cell Division Diagram
What would happen if an entire chromosome were missing or duplicated? What if a human had only 45 chromosomes? Or 47? This real possibility is usually due to mistakes during meiosis; the chromosomes do not fully separate from each other during sperm or egg formation. Specifically, nondisjunction occurs when homologous chromosomes or sister chromatids fail to separate during meiosis, resulting in an abnormal chromosome number. Nondisjunction may occur during meiosis I or meiosis II Most human atypical chromosome numbers result in the death of the developing embryo, often before a woman even realizes she is pregnant. Occasionally, a zygote with an extra chromosome can become a viable embryo and develop.
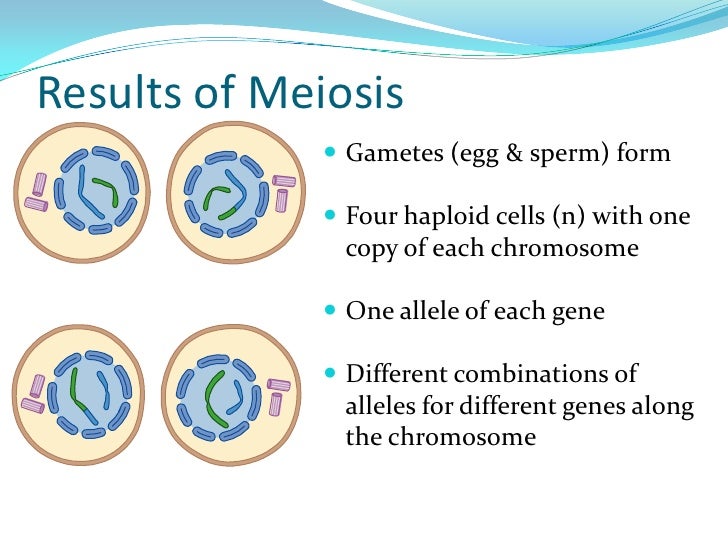
5 Stages Of Cell Division
Trisomy is a state where humans have an extra autosome. That is, they have three of a particular chromosome instead of two. For example, trisomy 18 results from an extra chromosome 18, resulting in 47 total chromosomes. To identify the chromosome number (including an abnormal number), a sample of cells is removed from an individual or developing fetus. Metaphase chromosomes are photographed and a karyotype is produced. A karyotype will display any abnormalities in chromosome number or large chromosomal rearrangements. Trisomy 8, 9, 12, 13, 16, 18, and 21 have been identified in humans. Trisomy 16 is the most common trisomy in humans, occurring in more than 1% of pregnancies. This condition, however, usually results in spontaneous miscarriage in the first trimester. The most common trisomy in viable births is Trisomy 21.
Trisomy 21: Down Syndrome
The Steps Of Cell Division
One of the most common chromosome abnormalities is Down syndrome, due to nondisjunction of chromosome 21 resulting in an extra complete chromosome 21, or part of chromosome 21 (Figure (PageIndex{4})). Down syndrome is the only autosomal trisomy where an affected individual may survive to adulthood. Individuals with Down syndrome often have some degree of mental retardation, some impairment of physical growth, and a specific facial appearance. With proper assistance, individuals with Down syndrome can become successful, contributing members of society. The incidence of Down syndrome increases with maternal age. The risk of having a child with Down syndrome is significantly higher among women age 35 and older.
